X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease with a strikingly heterogeneous clinical spectrum. Patients with X-ALD are asymptomatic at birth. Virtually all male patients with X-ALD eventually develop a progressive spinal cord disease (adrenomyeloneuropathy, AMN), with as the earliest symptom most often urge incontinence, followed by a spa…
White Matter Disorders
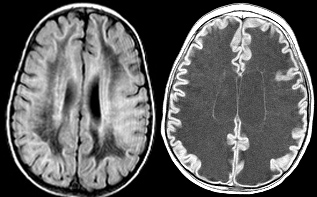
White Matter Disorders (WMDs) may occur at all ages and have many different causes. Adult WMDs are more often acquired, either inflammatory in young adults or related to vascular risk factors in elderly. Children most often suffer from genetic WMDs, the leukodystrophies. The overall incidence of WMDs in children is ~1:1000, similar to that of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) in adult…
Tuberous Sclerosis
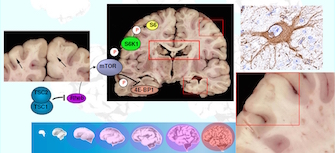
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) is an autosomal dominant disorder. TSC is characterized by benign tumors in the brain, kidney, heart, eyes, lungs and skin. Lesions in the brain, which includes cortical tubers and white matter abnormalities, are common and cause great problems for the patients and their families. TSC patients show mild learning disabilities to severe mental …
Schizophrenia

Schizophrenia is a chronic and debilitating brain disorder that affects about 1 percent of the population. It is characterized by delusional beliefs, hallucinations, disordered speech and deficits in emotional and social behavior, and is highly familial with heritability estimates of 81%. Genome-wide association and exome sequencing studies have shown that schizophre…
Rett Syndrome
Rett syndrome is a neurological disorder, diagnosed under the pervasive developmental disorders, affecting 1 in 10,000 girls. It is characterized by an initial period of seemingly normal post-natal development, up until 6-18 months, after which it is followed by an increasing manifestation of symptoms. These include deceleration in growth, loss of acquired motor and language…
Intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), mental retardation or (general) learning disability is a group of generalized disorders appearing before adulthood and affecting cognitive functioning and adaptive behaviors. Intellectual disability is defined as an intelligence quotient score under 70. The definition now includes both a component relating to mental functioning and one relating …
Epilepsy
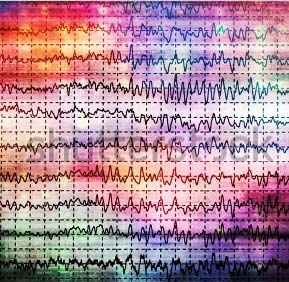
Epilepsy is a group of long-term neurological disorders characterized by epileptic seizures, sudden disruptions of the brain’s normal electrical activity accompanied by altered consciousness and/or other neurological and behavioural manifestations (generalised seizures, absence seizures or myoclonic seizures). Together, this group of disorders is one of the most common…
Depression
Depressive disorder involves changes in mood, thought and emotion and influences major aspects of daily life. It is one of the most common psychiatric disorders with a lifetime prevalence of ~20%. Current treatment strategies consist of medication, cognitive and behavioral therapy. None of these treatments can cure the disorder and most alleviate symptoms only in a subset of…
2024 © iPS Center. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy | Terms of Service

